
AI is transforming from a supportive system to an autonomous decision maker. The agentic AI systems that can do things on their own with minimal human supervision are revolutionizing the industry in the medical fields as well as finance. But alongside this advantage, there is a pressing situation, and that is the issue of data privacy and security.
As AI agents become more autonomous in their operations, they tend to utilize large volumes of personal and corporate information. Here, an essential question is: How to balance AI autonomy and data security? Here, we shall explore the nexus point between Agentic AI and data privacy, highlight the main risks, and offer ways to make AI agents trustworthy, bringing both autonomy and user trust.
Understanding Agentic AI
Agentic AI is capable of making decisions, learning from feedback, and acting on its own, unlike traditional AI, which does not follow a set of rules. Imagine self-driving cars going through the traffic, robot-based financial advisors giving investment advice, or medical agents prescribing individualized medicine. Although these capabilities open the door to efficiency, they also raise the issue of AI autonomy and security, particularly with sensitive information. McKinsey estimates that this emerging technology has the potential to generate $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion in additional value on top of the value potential of traditional AI.
The Data Privacy Challenge in Agentic AI
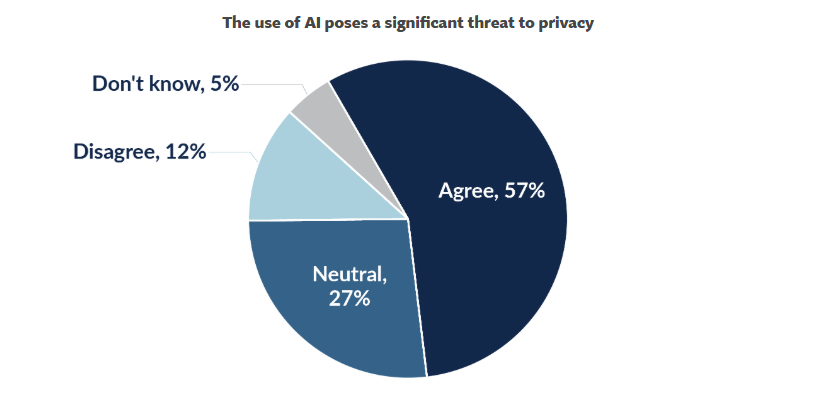
Autonomous systems require constant access to personal, behavioral, and contextual information to operate successfully. Nonetheless, this dependence on large datasets poses privacy threats.
- Huge Data Reliance – Agentic AI utilizes large volumes of user data to train and operate. This expounds exposure to abuse.
- Unmonitored choices – Autonomous AI could process data in a manner that it did not agree to.
- Ethical Dilemmas – Is an AI agent allowed to put efficiency over privacy?
This is where AI solutions with a focus on privacy are required. Users are likely to lose their identities and be spied on without the appropriate security control measures in place. In the case of enterprises, it may involve a breach of compliance and negative publicity.
Security Risks in Agentic AI Systems
In addition to privacy, data protection on AI systems is at risk due to several cybersecurity attacks:
- Adversarial Attacks: Hackers alter the inputs of AI, which encourages the system to make invalid decisions.
- Data Poisoning: Attackers corrupt the datasets on which AI agents are based.
- Unauthorized Access: There is a leakage of sensitive data due to a lack of advanced security controls.
- Self-directed Risk-Taking: AI agents can take actions without regard to the ethical or safety consequences.
Real-life examples of these dangers
- An AI chatbot accidentally leaks the confidential data of users.
- Autonomous cars that gather non-transparent geolocation data.
These examples highlight the need to address the AI risk management and privacy issues. Business organizations cannot afford to make the safe development of AI agents optional but fundamental.
Balancing Autonomy and Security: Key Strategies
In order to deal with such risks, companies should consider AI ethics and privacy protection at all levels of their development. The following are innovation and responsibility balancing strategies:
1. Human-in-the-Loop Approach – Checkpoints that allow human beings to examine important decisions should also be present even in autonomous agents. This constrains the blind faith in AI products.
2. Minimization of Data and Anonymization – Gather only the data that is necessary. Exposure of personally identifiable information is minimized when using anonymization techniques.
3. Explainability and Transparency – Users and regulators need to understand the manner in which AI arrives at its conclusions. The use of explainable AI systems creates trust.
4. Strong Cybersecurity Standards – Protecting the data in AI systems is essential, which is done by encryption, secure APIs, and advanced monitoring tools.
5. Adaptive Governance Models – The enterprise AI development services should correspond to the changing privacy laws, such as GDPR and CCPA. This ensures compliance while ensuring freedom.
Using these measures, companies can develop AI privacy-centered solutions that integrate both autonomy and trust. To know more about why enterprises are betting big on AI Agents, explore our blog.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
The future of Agentic AI is being shaped by governments and organizations across the globe through strict compliance frameworks:
- GDPR/CCPA – Restrict the collection, storage, and processing of personal information.
- New AI Rules – The EU AI Act proposes stringent regulations on risky AI systems.
- AI Ethics Frameworks – International regulations emphasize fairness, accountability, and transparency.
As a firm, it implies that it is not enough to create trustworthy AI agents using technical protective measures, but through active compliance. An AI Agent development company that incorporates regulatory foresight into the process is a trusted partner.
The Future of Agentic AI and Data Privacy
With the development of AI technology, the issue of autonomy and security is going to be at the center stage. Future innovations are directed at:
- Privacy-Saving AI Technologies: Federated learning and differential privacy are some of the techniques that help AI to learn without centralizing sensitive information.
- Ethical AI Design: Integrating decision-making principles that emphasize privacy protection into the main logic of the agent.
- Trust-Centric Adoption: AI ethics and privacy protection will bring more users and partners to enterprises that take care of them.
Over the next few years, companies that are interested in the secure development of an AI agent will increasingly outsource to a specialized partner, such as an Agentic AI development company, or opt to hire AI developers who are knowledgeable in security-first methodologies.
Conclusion
Agentic AI and data privacy are two sides of a coin; the first one is an aspect of innovation and independence, and the other part assures trust and safety. Lacking powerful privacy-related AI solutions, autonomy might result in abuse and violations, as well as unethical actions.
Businesses should understand that the process of balancing autonomy and data protection is not a single exercise. Businesses can develop responsible and innovative AI agents by investing in AI risk management and privacy solutions to create trustworthy AI agents. Gartner predicts that by 2029, agentic AI will autonomously resolve 80% of common customer service issues.
For companies that are willing to be ahead in the future, collaborating with an AI agent developing firm or consulting AI development services will enable them to have autonomous systems for data protection and align with ethical standards.



